Aufgabe:
In einer zylindrischen Feldspule mit n = 600 Windungen und der Länge l = 45 cm befindet sich eine kurze Induktionsspule mit nind = 2400 Windungen und Aind = 6,8 cm^2.
Berechnen Sie die Zeit At, in der die Stromstärke in der Feld-spule gleichmäßig von 0 auf 1 A anwachsen muss, damit in der Induktionsspule eine Spannung von Und = 5 mV induziert wird.
Problem/Ansatz:
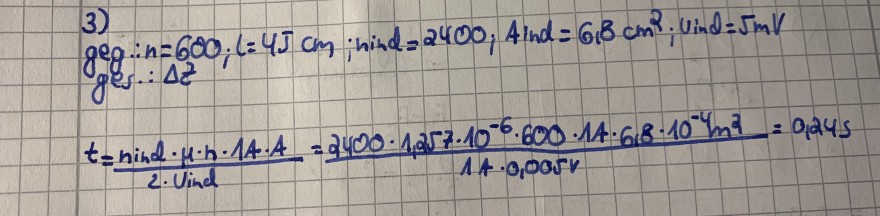
Text erkannt:
3)
\( \begin{array}{l} \text { geg: } n=600 ; \text { L }=45 \mathrm{~cm} \text {; hind }=2400 ; \text { Aind }=6,8 \mathrm{~cm}^{2} \text {; Vind }=5 \mathrm{mV} \\ g \text { J.: } \Delta z \\ t=\frac{\text { ind } d \cdot \mu \cdot h \cdot 14 \cdot A}{2 \cdot \text { Vind }}=\frac{2400 \cdot 1,257 \cdot 10^{-6} \cdot 600 \cdot 14 \cdot 618 \cdot 10^{-4} \mathrm{~m}^{2}}{14 \cdot 0,005 \mathrm{~V}}=0,245 \end{array} \)
Die Formel dafür und das Ergebnis habe ich bereits. Ist das Ergebnis richtig?
Jedoch würde ich gerne verstehen wollen, wie man auch die Formel kommt, damit ich es nachvollziehen kann. Ich würde mich sehr freuen, wenn mir das jemand genau erklären könnte.